Ball Valves and Check Valves For Pressure Washers

Figure 1: Pressure washer
Pressure washer valves manage the flow and pressure of water within the system, ensuring both performance and safety. These valves, such as check valves and ball valves, are designed to handle high pressures and varying temperatures. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the main pressure washer valves, focusing on their roles, selection criteria, and maintenance requirements.
Table of contents
- How does a pressure washer work
- Pressure washer ball valves
- Pressure washer check valves
- How to select pressure washer valves
- Check valve issues in a pressure washer
View our online selection of ball valves and check valves
How does a pressure washer work
A pressure washer uses high water pressure to remove dust, mold, loose paint, grease, and stains from surfaces. The main parts of an electric pressure washer are:
- Water and detergent inlet: The process begins with two separate inlets. Cold water is supplied from a faucet (Figure 2 labeled G) through a hose. It passes through an inline filter to remove impurities. Detergent is drawn from a container (Figure 2 labeled A) through a dedicated hose.
- Ball valve: A ball valve may be installed at the water inlet to manually control the water flow into the pressure washer. This allows the user to start or stop the water flow as needed.
- Water pump: The high-pressure pump (Figure 2 labeled B) draws in the detergent and water, mixing them in precise proportions. The pump pressurizes the mixed and heated solution.
- Ball valve: A ball valve is installed between the pump and the cleaning nozzle. This allows the user to start or stop the water flow as needed, providing an isolation function for maintenance or when the machine is not in use.
- Check valve: Check valves (Figure 2 labeled D) are typically installed at the faucet and pump outlets.
- High-pressure exit hose: The mixture of water and detergent from the pump is directed through a high-pressure exit hose (Figure 2 labeled E).
- Nozzle: The end of the hose has a narrow nozzle (Figure 2 labeled F), which further increases the pressure of the exiting water jet.
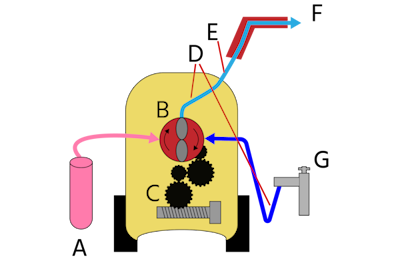
Figure 2: Main parts of an electric pressure washer: Detergent inlet (A), water pump (B), electric motor (C), ball valve (D), high-pressure exit (E), check valve (F), and faucet (G). The image does not show other parts, like an inline filter and unloader valves.
Pressure washer ball valves
Ball valves are quarter-turn shutoff valves with a hollow, perforated ball to control water flow. When open, the ball aligns with the flow direction, allowing water to pass through; when closed, it blocks the flow.
Ball valves are typically lightweight and are a non-intrusive addition to pressure washers. Also, ball valves have non-linear flow characteristics. Slightly closing the valve can create a high-pressure spray, which is effective for rinsing surfaces thoroughly. Read our ball valve overview article for more information on the design, working, and various types of ball valves.
What does a power washer ball valve do?
Pressure washer ball valves are installed on the high-pressure hose between the pump and cleaning tools. They allow quick tool changes, like spray guns and surface cleaners, without shutting off the machine, which is useful when main controls are hard to access, such as at heights or remote locations. Ball valves control the fuel supply by allowing operators to quickly shut off or open the flow to the engine in fuel-powered washers.

Figure 3: Stainless steel ball valve
Pressure washer check valves
A check valve allows fluid to flow in only one direction, preventing backflow. It operates automatically, using the fluid's pressure to open and close. There are various types of check valves, like swing, spring-loaded, lift, and ball check valves, each with specific mechanisms for allowing or blocking flow. Read our check valve overview article for more information on the design, working, and typical applications of check valves.
What does a pressure washer check valve do?
A check valve for a pressure washer is typically located in two main areas:
- Inlet side (Low-pressure check valves): These are located at the lower end of the pump. They allow water to enter the pump from the inlet while preventing it from flowing back.
- Outlet side (High-pressure check valves): These are located at the upper end of the pump. Their role is to allow pressurized water to exit the pump while preventing it from flowing back into it.

Figure 4: Stainless steel check valve
How to select pressure washer valves
-
Material: Pressure washer valves are commonly made of stainless steel or brass.
- Stainless steel: Ideal for high-pressure applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
- Brass: Brass is commonly used for corrosion resistance and durability, especially in residential and light commercial pressure washers.
- Pressure rating: Ensure the valve is rated to handle the maximum system pressure, up to 276 bar (4,000 psi) or more for high-performance pressure washers.
- Temperature rating: In many pressure washers, water is heated to 50 to 70 𐩑C (125 to 155 𐩑F) to improve cleaning. Valves should be able to withstand the expected temperature range.
- Flow coefficient (Cv): Select a valve with a flow coefficient (Cv) rating that matches the flow requirements of your system. Use our Cv calculator to determine the flow coefficient from the rated flow values in the washer manual.
- Seal material: PTFE and EPDM are ideal due to their resistance to water and steam. Read our chemical resistance guide for more information on the compatibility of various housing and seal materials with different media.
Check valve issues in a pressure washer
When a hose is connected to a pressure washer and no water flows through, the issue is often a blocked or stuck check valve at the water inlet. This can occur due to debris or water deposits, especially if the pressure washer is improperly maintained.
Perform the following steps to troubleshoot a pressure washer check valve:
- Remove the water inlet fitting: Start by checking the inlet check valve, located where the water supply hose connects to the pressure washer. Use a wrench to remove the inlet fitting, giving you access to this check valve.
- Inspect the check valve and spring: Check for any debris or deposits causing the valve to stick. Ensure the spring (if present) is intact and functioning correctly.
- Clean or replace components: If the check valve is stuck, clean it thoroughly. If cleaning does not resolve the issue, replace the check valve.
- Apply grease: Before reassembling, apply a small amount of grease to the o-rings on the check valve to ensure a good seal.
- Reassemble: Reassemble the components, ensuring everything is securely in place. If applicable, apply a small dab of Loctite on the threads.
- Check the outlet check valve (if necessary): If the issue persists, check the outlet check valve, where the high-pressure hose connects to the pressure washer. Follow similar steps to inspect, clean, or replace this valve.










