Pneumatic Hoses and Tubing Explained
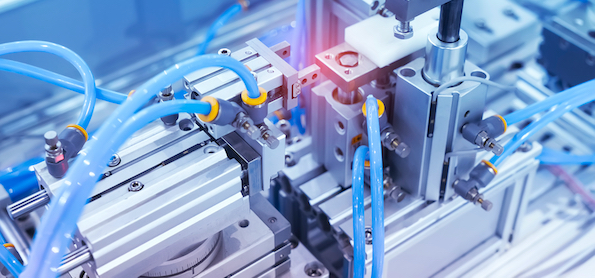
Figure 1: Pneumatic components like valves, cylinders, or pressure regulators are typically connected to the main air supply line via flexible tubing or hoses.
Pneumatic tubes and hoses transport compressed air from storage to where it is needed. They enable the operation of machinery, actuation of controls, and transportation of materials or samples with efficiency and precision. This article covers the basics of pneumatic hoses and tubing. It discusses their design, their uses, and how to choose the right ones.
Table of contents
- Understanding pneumatic hoses and tubing
- Distribution in pneumatic systems
- Materials
- Selecting a hose or tube for a pneumatic system
- FAQs
View our online selection of hoses!
Understanding pneumatic hoses and tubing
Pneumatic systems use hoses and tubing to move air or fluids. Hoses are flexible for environments with significant movement. Tubing is rigid, making it good for fixed routes. Knowing the inner and outer diameters helps choose the right one for an application.
Pneumatic hoses
Hoses can handle high pressures and are ideal for situations where connections must be frequently disconnected and reconnected. They are typically more robust and flexible. Hoses are specified by their inner diameter (ID). This dimension controls the volume of air or fluid that can pass through the hose, affecting the flow rate and pressure.
Hoses typically come with fittings pre-attached at both ends. Control circuits for cylinders and actuators often use tubes with smaller diameters, typically between 3.2 mm and 9.5 mm (1/8 inch to 3/8 inch). They are preferred for more demanding applications and are frequently handled and transported across factory and workshop environments.
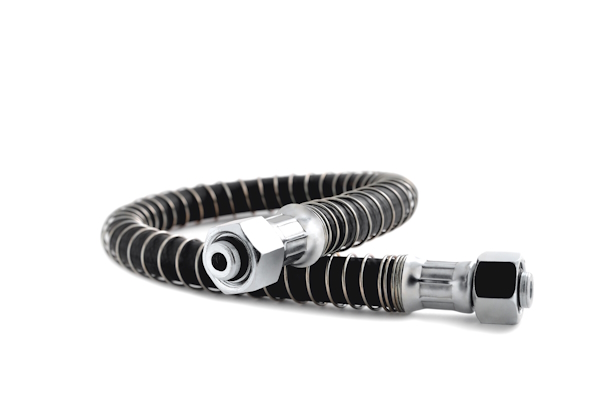

Figure 2: A pneumatic hose
Pneumatic tubing
Tubing is stiffer than hoses and is typically used if the air supply route will not change and connected parts will not move. Tubing is typically specified by its outer diameter (OD). Typical tubing outer diameters for main air supply lines range from 6.3 mm to 12.7 mm (1/4 inch to 1/2 inch).
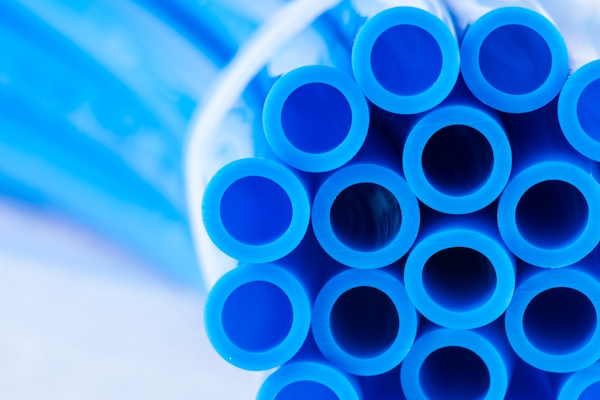

Figure 3: Polyurethane air tubes
Distribution in pneumatic systems
The operation and performance of pneumatic systems rely on how effectively compressed air moves from the source to other components (e.g., actuators, valves, and tools). Air can be moved through rigid or flexible air compressor tubing or hosing.
Rigid pipework for air distribution
In big industrial spaces, strong pneumatic pipes are used to transport compressed air. These pipes are durable and can resist the bumps often seen in busy workshops. These pipes are made from sturdy materials like aluminum, copper, stainless steel, or rigid PVC to last a long time. However, installing these pipes can be challenging due to:
- Labor intensive and costly
- Potential for leaks
- Environmental sensitivity
Flexible hoses
For smaller setups or temporary installations, flexible hoses present a versatile and adaptable alternative to rigid pipework. Made from materials like light HDPE or strong rubber, flexible hoses are tough enough for industrial use.
They are also much easier to put in and change. Their flexibility is very useful in places where air lines need to move or be adjusted often. This helps reduce the number of fittings needed and makes the system less affected by temperature changes.
Connections to pneumatic components
The final step in an air supply system is connecting to pneumatic parts that manage the main air flow, such as valves, cylinders, and pressure regulators. Pneumatic hoses and tubes connect to appliances via fittings, specifically designed to ensure a secure and leak-proof connection. These fittings come in various types, including push-to-connect, compression, and threaded fittings.
Push-to-connect fittings offer quick installation and removal, ideal for systems requiring frequent modifications. Compression fittings create a strong seal for high-pressure applications. Threaded fittings provide a secure connection in systems that do not move.
Materials
Hoses can be constructed from multiple layers, including a nylon braid sandwiched between the inner and outer layers. This design enhances durability and ensures the hose can withstand various operational challenges. The inner material must be resistant to oils and condensate, while the outer material should protect against atmospheric conditions.
Table 1: Materials for pneumatic tubes and hoses
| Material | Description |
|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Durable and highly resistant to wear and tear, this material combines the properties of plastic and rubber. It is known for strength, flexibility, resistance to kinks and chemicals, and can handle pressures over 10.3 bar (150 psi). |
| Polyethylene | Preferred for direct piping, good for low-pressure situations, may kink, can handle up to 9.3 bar (135 psi), affordable, lightweight, and chemically neutral, with a limited temperature range. |
| Silicon | Known for outstanding thermal stability and flexibility, this material is perfect for high-temperature uses. It resists weathering and ozone, performs well over a wide temperature range, can handle up to 6.9 bar (100 psi), is chemically inert, and suits medical and food-grade applications. |
| Polyamide | Known for its excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, offers high resilience and toughness, suitable for high-pressure applications, typically rated for pressures up to 13.8 bar (200 psi), exhibits good chemical resistance, lightweight, and maintains performance in a broad temperature range |
Selecting a hose or tube for a pneumatic system
This section gives detailed descriptions of the factors to consider when choosing a hose or tube for a pneumatic system.
Application requirements
- Operating pressure: Know the maximum operating pressure of the system. Hoses and tubes, including air compressor hoses, have different pressure ratings. Choosing one that cannot withstand the system's pressure can cause failures.
- Temperature range: Consider the temperature range within which the system will operate. Some materials can become brittle and crack in cold temperatures, while others may soften and deform under high heat.
- Media: Identify the type of media (air, water, oil, etc.) that will flow through the hose or tube. Some materials are better suited for certain types of media due to chemical compatibility. For instance, an air hose is specifically designed for air media. Read our chemical compatibility guide to learn more.
- Environment: Consider external elements such as exposure to chemicals, UV light, abrasion, and extreme temperatures, as they can impact the lifespan and performance of a hose or tube.
Hose vs tube
- Flexibility: Hoses, like air line hoses, are generally more flexible than tubes, making them ideal for moving parts or applications where the hose needs to be routed around obstacles.
- Cost: Tubes are often less expensive than hoses and are a cost-effective solution for applications where flexibility is not a critical factor.
- Installation: Consider the ease of installation. Tubes can be easier to install in tight spaces due to their rigidity.

Figure 4: A coiled hose is often used in workshops with pneumatic tools
Air hose size and length
- Inner diameter (ID): The ID should be large enough to handle the flow rate without causing excessive pressure drop but not so large as to be unnecessarily bulky or expensive. When choosing between 1/4 vs 3/8 air hose, consider the flow requirements and pressure drop.
- Length: Consider the length needed for the application, including allowances for bending and routing. Avoid unnecessary length that can lead to pressure drops and potential entanglement or damage. An air compressor hose size chart can be helpful in determining the appropriate length and diameter.
Special requirements
- Anti-static properties: In environments where static electricity is a concern, consider hoses or tubes with anti-static properties.
- Customization: For highly specialized applications, manufacturers can produce custom hoses and tubing that meet specific dimensions, pressure ratings, and material requirements. This includes hoses with several layers, reinforced walls for extra strength, or built-in conductive wires for static discharge in areas where static electricity might be dangerous.
- Standards and certifications: Pneumatic hoses and tubing must often meet specific industry standards and certifications to ensure they are safe and effective for their intended use. These can include standards related to food safety, medical use, or flame resistance, among others.
- Safety factors: Pneumatic hoses and tubing are designed with a safety factor, typically ranging from 3:1 to 4:1. This means that the burst pressure of the hose or tube is three to four times higher than the maximum operating pressure. This safety factor is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the system's integrity under unexpected conditions.
FAQs
What is pneumatic tubing?
Pneumatic tubing transports compressed air to operate pneumatic tools and systems, made from materials like polyurethane or nylon.
How do you maintain compressed air tubing?
Regularly inspect for leaks, ensure proper installation, and replace damaged or worn sections.
What is the difference between a 1/4 vs 3/8 air hose?
A 1/4 air hose is lighter and more flexible, suitable for low-demand tools, while a 3/8 air hose provides more airflow for high-demand tools.
How do I choose the right air compressor hose size?
Choose an air compressor hose size based on the required airflow, the distance from the compressor, and the tool's air consumption.





