Poppet Valve vs Spool Valve


Figure 1: Figure 1: A pressure control valve using poppet design (left) and a hydraulic directional spool valve (right)
Pneumatic and hydraulic control valves are available in poppet or spool configurations. Both valves can be operated manually, electrically, or pneumatically, but the choice between a poppet or spool valve depends on the required flow control, leakage tolerance, and system complexity.
- Poppet valves are ideal for precise control and high flow applications with fast response and low maintenance needs.
- Spool valves are suitable for consistent response, complex flow paths, and vacuum applications, with the ability to hold pressure downstream.
This article discusses the differences between poppet and spool valves and when to choose one.
Table of contents
- Poppet valve features
- Spool valve features
- Difference between poppet valve and a spool valve
- How does a poppet valve work?
- How does a spool valve work?
- FAQs
View our online selection of pneumatic and hydraulic solenoid valves!
Poppet valve features
Table 1: Poppet valve features
| Advantages | ✅ Lower cost ✅ Less susceptible to contamination and low maintenance requirements ✅ Fast response time ✅ Closed crossover. The poppet seals the exhaust before allowing flow, preventing intermediate states and ensuring precise control during switching. ✅ Higher flow rate due to large internal surface area ✅ Lower friction and longer life due to less wear on internal seals |
| Disadvantages | ❌ Back pressure can open the valve if supply pressure is removed; hence, not ideal for maintaining pressure downstream. ❌ Requires high force to actuate due to spring tension and air pressure. ❌ Not balanced; pressure must be applied beneath the poppet to keep it non-actuated. ❌ Not recommended for vacuum applications. |
Spool valve features
Table 2: Spool valve features
| Advantages | ✅ Less force required to actuate the valve ✅ Spool valves are balanced; the pressure entering the valve from any port does not influence the spool's motion. ✅ Constant response time ✅ Actuation force unaffected by changes in operating pressure ✅ Can be used to lock pressure downstream ✅ More complex flow paths, 4-way functionality |
| Disadvantages | ❌ Lower flow rate due to lower internal surface area ❌ Open crossover (All ports briefly open during spool actuation, allowing fluid flow) ❌ Seals on the spool wear over time, reducing lifespan ❌ More susceptible to contamination ❌ Requires high maintenance ❌ Higher cost |
Difference between poppet valve and a spool valve
Table 3: How to select a poppet or spool valve for an application
| Key parameter | Poppet valves | Spool valves | Notes |
| Precise control | ✔️ | Closed crossover | |
| High flow volume | ✔️ | Increased internal area allows for higher flow rates. | |
| Long life | ✔️ | Less wear on internal seals and fewer precision parts contribute to longer life. | |
| Rapid response | ✔️ | Quick activation with reduced stroke length | |
| Budget-friendly | ✔️ | Less costly due to less precision manufacturing required | |
| Vacuum | ✔️ | Suitable for vacuum applications | |
| Maintain downstream pressure | ✔️ | Desirable because back pressure can actuate a poppet valve when supply pressure is absent. | |
| Selector valve | ✔️ | Suitable for high and low pressure, or vacuum and pressure applications | |
| Consistent response time | ✔️ | Changes in pressure have less effect on response time. | |
| Valve function | ✔️ | Available in 2, 3, or 4-way configurations | |
| Versatility | ✔️ | Can be normally-open, normally-closed, selector, or diverter |
How does a poppet valve work?
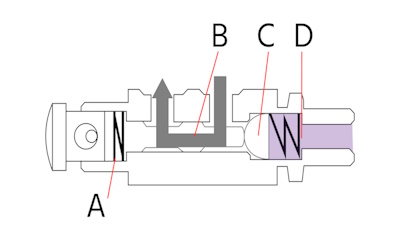
Figure 2: Poppet valve design: spring (A), stem (B), poppet (C), and spring (D).
Poppet valves have a movable part, the 'poppet' (Figure 2 labeled C), that fits snugly against a valve seat to control flow. When the poppet lifts from the seat, typically due to pressure changes or an actuating force, it clears the path for fluid to pass through. A spring (Figure 2 labeled A) returns the poppet to its resting position, creating a seal and stopping the flow. This movement makes poppet valves reliable and excellent for creating tight seals with minimal leakage.
This design also offers a range of benefits over spool valves, making it more appropriate for specific uses. Applications that demand exact control, significant flow capacities, extended durability, minimal leakage, quick reaction times, or affordability often opt for poppet valves.
How does a spool valve work?
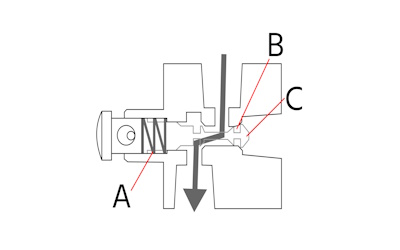
Figure 3: Spool valve design: spring (A), seals (B), and spool (C).
Spool valves feature a cylindrical spool (Figure 3 labeled C) that slides back and forth within a sleeve or housing. This spool is precision-machined with grooves and lands (the raised portions between grooves) that align with ports in the valve body as it moves. When the spool shifts, it connects or disconnects these ports, directing fluid flow accordingly. The seals around the spool (Figure 2 labeled B) are critical, often o-rings, to prevent leakage.
Due to their design, spool valves can manage more complex flow paths, making them versatile for various applications, including directional control in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. When compared with poppet valves, spool valves present distinct benefits and drawbacks. They are more suitable for applications involving vacuum environments, applications that need to maintain downstream pressure, selector valve functions, and situations where a uniform response time is critical.
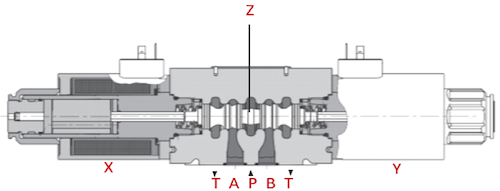
Figure 4: Components of a 4/3-way hydraulic solenoid valve: spool (Z), solenoid on either side (X and Y), and ports (T, A, P, B)
Read our pneumatic and hydraulic valve overview articles for more details on how these valves work.
FAQs
How does a pneumatic poppet valve work?
A pneumatic poppet valve uses air pressure to move a poppet away from a seat, allowing air to flow through and springs back to close when pressure drops.
Where are spool valves used?
Spool valves are used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems to control the flow and direction.
What is the difference between a poppet and spool valve?
Poppet valves use a movable disk/cone to seal against a seat, offering quick response and tight sealing. Spool valves use a sliding spool to direct flow, allowing complex control with multiple paths.







