Hydraulic Ball Valves For High Pressures

Figure 1: 2-way hydraulic ball valve with cutting ring
Hydraulic ball valves regulate, direct, and control the flow of hydraulic fluids by utilizing a spherical closure unit with a central bore. Hydraulic ball valves often work in high-pressure applications, so these valves can handle pressure up to 500 bar (7,250 psi), ensuring reliable performance and safety in demanding conditions. They are operated with a handle and provide unobstructed flow due to the full-bore design. These ball valves are suitable for hydraulic and heating oils within a temperature range from -10 to 80 𐩑C (14 to 176 𐩑F). This article explores the technical features and specifications of manual high-pressure hydraulic ball valves.
Table of contents
- Circuit function
- Connection type
- Materials
- Bore size
- Maximum pressure difference
- Compliance with standards
- Hydraulic ball valve symbol
- Hydraulic operated ball valve applications
View our online selection of hydraulic ball valves!
Circuit function
The hydraulic ball valve can be 2-way or 3-way.
- 2-way: 2-way valves are suitable for simple on/off control in a single flow path. They are commonly used in applications where fluid needs to be started or stopped.
-
3-way:3-way valves are suitable for applications requiring flow diversion, mixing, or alternating between two outlets. They are ideal for systems needing more versatile flow management. 3-way valves can have T- or L-flow paths.
- T-port: Connects three paths, allowing flow to be mixed or diverted. Ideal for directing flow to multiple outlets.
- L-port: Connects two paths simultaneously, switching flow between two outlets. Suitable for simple flow alternation.
Read our ball valve circuit function article for more information on common ball valve circuit functions.
Connection type
The ports have female threads, known as BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel), or cutting ring connections, per ISO 8434-1 standards.
- The BSPP threaded ports are available in sizes ranging from G 1/8 inch to G 2 inch.
- The sizes for cutting ring connections range from 6 to 28 mm for the light load class (L) and 8 to 30 mm for the heavy load class (S).

Figure 2: 3-way hydraulic threaded ball valve
Materials
-
Valve housing:The valve housing is typically made of zinc-plated steel or nickel-plated brass.
- Zinc-plated steel: This material can withstand pressures up to 500 bar (7252 psi). The material is corrosion-resistant, durable, and suitable for harsh environments.
- Nickel-plated brass: This material can withstand pressures up to 210 bar (3046 psi).
- Ball: The ball is made of hard chrome-plated steel or chromium-plated brass. These materials have improved wear resistance, ensuring a tight seal and smooth operation over many cycles.
-
Seals:The seal comprises POM, NBR, FKM, or PTFE.
- Polyoxymethylene (POM): POM has high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, which is ideal for hydraulic applications.
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR): NBR works well with neutral liquids such as water or hydraulic oil.
- FKM (Fluorine Rubber, Viton): FKM is recommended for (compressed) air, oils, and fuels.
- Teflon (PTFE): PTFE is resistant to almost all hydraulic fluids. The material is hard, making it suitable for higher operating pressures and temperatures.
- Handle: The straight handles are made from die-cast zinc for valve sizes up to DN 16. For larger valve sizes (above DN 16), they are made from aluminum. Aluminum is chosen for its lightweight properties, which make it easier to operate larger valves without compromising strength.
Read our chemical resistance guide for more details on the compatibility of various materials with different media.
Bore size
The valve bore size refers to the internal diameter of the passage through which fluid flows. It determines the valve's flow capacity. A larger bore size allows for higher flow rates, while a smaller bore size restricts flow. Bore sizes from 4 to 50 mm are typically available for hydraulic ball valves.
Maximum pressure difference
The maximum pressure difference is the highest pressure differential between the valve's inlet and outlet without compromising performance or safety. Steel hydraulic ball valves are suitable for high-pressure applications up to 500 bar (7,250 psi), and brass valves can operate up to 210 bar (3046 psi).
Compression class refers to the pressure rating of the valve, which indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle safely. This is typically denoted by "PN" (Pressure Nominal) followed by a number, such as PN 400 or PN 350. For example, PN 400 means the valve is rated to handle a maximum pressure of 400 bar.
Compliance with standards
Hydraulic ball valves comply with DIN EN ISO 8434-1 (DIN 2353), a standard that outlines requirements for metallic tube connections in fluid power systems.
Hydraulic ball valve symbol
Figure 3 shows a hydraulic actuated ball valve symbol. A 2-way ball valve is represented by two equilateral triangles pointing toward each other with a ball at the center. The 'H' label signifies the valve is suitable for hydraulic applications.
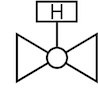
Figure 3: Hydraulic ball valve symbol
Hydraulic operated ball valve applications
High-pressure hydraulic ball valves are essential in various industries to manage hydraulic fluid flow under extreme conditions.
- The oil and gas sector uses hydraulic ball valves to manage the flow of crude oil and natural gas in subsea operations and wellhead control.
- Industrial hydraulic systems use hydraulic ball valves to regulate hydraulic fluid in press machines and injection molding processes.
- In aerospace and defense, they control hydraulic flow in aircraft landing gear and missile launch systems.
- In marine and offshore applications, they manage water flow in ballast systems and are used on offshore platforms for control and safety functions.
Read our high pressure hydraulic ball valve applications article for more information on the various applications of high-pressure hydraulic ball valves.







