Cutting Ring Fitting - How It Works

Figure 1: Cutting ring fittings provide durable, leak-proof connections.
Cutting ring fittings offer leak-proof seals and are suitable for various industrial applications, like hydraulics and pneumatics. This fitting's components are engineered to mechanically lock together, with the cutting ring being compressed and biting into the tubing to form a robust, high-pressure seal. This article overviews the design of a cutting ring fitting, how it works, its advantages, and its applications.
Table of contents
- Components of a cutting ring fitting
- Installing a cutting ring fitting
- Applications of cutting ring fittings
- Advantages
- Maintenance and troubleshooting of a cutting ring fitting
- FAQs
View our online selection of cutting ring fittings!
Components of a cutting ring fitting
As seen in Figure 2, cutting ring fittings, also known as ferrule fittings, consist of three primary components: the fitting body, the cutting ring (ferrule), and the nut:
- Fitting body (A): The fitting body houses the other components and comes in various shapes to make different connection types possible (e.g., straight, elbow, tee).
- Cutting ring (B): The cutting ring, also called a ferrule, is made of harder material than the tubing it cuts into and is responsible for the fitting's sealing action.
- Nut (C): The nut enables the assembly and disassembly of the fitting. It is a threaded component that applies compressive force to the cutting ring.
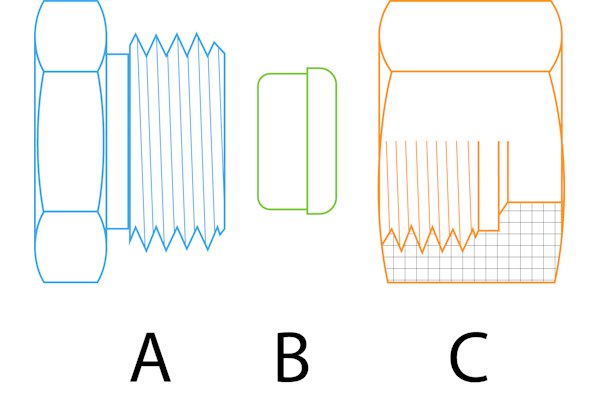
Figure 2: The components of a cutting ring fitting: body (A), cutting ring (B), and nut (C).
Installing a cutting ring fitting
Proper installation is critical to ensure the integrity of the connection and prevent leaks. Follow these steps to install a cutting ring fitting correctly:
-
Preparation
- Select the correct size of the cutting ring fitting for the tubing.
- Ensure the tube end is cut squarely.
- Remove burrs, sharp edges, and any other foreign material from the tube end.
-
Assembly
- Slide the nut (Figure 3 red) onto the tube (Figure 3 blue) with the threads facing outward.
- Place the cutting ring (Figure 3 black) on the tube, ensuring it is seated correctly.
- Insert the tube into the fitting body (Figure 3 orange) up to the stop point. The tube end should hit against the shoulder inside the fitting to establish the correct insertion depth.
-
Tightening
- Hand-tighten the nut onto the fitting body to ensure the threads are properly engaged.
- Use a pair of wrenches to hold the fitting body and turn the nut. Tighten the nut according to the manufacturer's specifications.
- The cutting ring presses into the tube as the nut is tightened, creating a sharp bite that seals the tube to the fitting body. This is the critical cutting action that gives the fitting its name.
-
Final check
- Conduct a pressure check on the fitting. Ensure there are no leaks at the recommended operating pressure.
- If the fitting is leaking, slightly tighten the nut. However, stay within the recommended torque.
-
Later assemblies
- If the fitting is disassembled and reassembled, the nut usually requires less torque to achieve a seal.
- A cutting ring fitting's cutting action can diminish after multiple reassemblies. Inspect the fitting and tubing for any signs of damage before reusing.
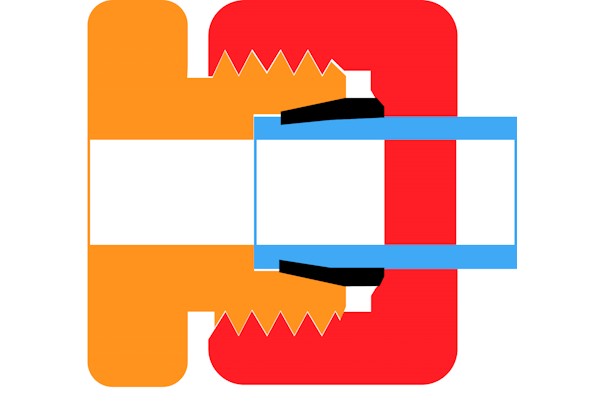
Figure 3: Complete assembly of a cutting ring fitting
Applications of cutting ring fittings
Cutting ring fittings are versatile connectors used across various industries due to their robustness, reliability, and ease of assembly. Below are some common applications of cutting ring fittings:
- Hydraulic systems: Hydraulic systems need high-pressure connectors to prevent leaking and other issues. These are used for hydraulic pumps, valves (e.g., hydraulic solenoid valve), cylinders, and other components. Learn more in our hydraulic fittings article.
- Pneumatic systems: Cutting ring fittings are found in applications that transport compressed air, such as pneumatic control systems, air brakes, and HVAC systems.
- Automotive industry: Cutting ring fittings are found in vehicles' brake lines and fuel systems.
- Water treatment plants: Cutting ring fittings are used in systems that transport and regulate water and treatment chemicals.
- Manufacturing equipment: Pneumatic and hydraulic lines that power factory automation, machinery, and robotics can have high-pressure requirements.
- Food and beverage industry: Cutting ring fittings can be used in systems that process and transport food-grade liquids. They must be made of materials that comply with food safety standards.
Advantages
- Leak-proof seal: The cutting action of the ferrule ensures a tight, mechanical seal that is highly resistant to leaks. The metal-to-metal seal is capable of withstanding significant pressure variations and thermal cycles.
- Ease of installation: No need for flaring, soldering, or welding, which simplifies the installation process and reduces the time required. They can be assembled with standard hand tools, making them suitable for use in the field or confined spaces.
- Reusability: While the cutting ring is deformed upon the first installation to create the seal, the fitting can often be disassembled and reassembled multiple times with the assurance of a good seal, providing cost savings in maintenance and repair scenarios.
- Vibration resistance: The mechanical grip of the ferrule on the tube provides excellent resistance to loosening caused by vibration, making these fittings suitable for mobile machinery and high-vibration environments.
- High-pressure capability: Designed to withstand high-pressure applications, cutting ring fittings are commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems where other fittings might fail.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, from hydraulic systems in industrial machinery to pneumatic controls in automation. Compatible with multiple types of tubing, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and copper.
- Material compatibility: Available in multiple options for different environmental conditions and fluid compatibility requirements. Common materials include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and brass for lower-pressure, less corrosive environments.
- Compact design: The small footprint of cutting ring fittings makes them an ideal choice for installations where space is limited. Their compact nature does not significantly affect the flow characteristics in the system.
- Safety: By providing a secure connection that can handle high pressures without bursting or leaking, cutting ring fittings contribute to the system's overall safety. The lack of welding or open flames during installation reduces the risk of accidents during assembly.
- Cost-effective: The reduction in labor costs due to quick and easy installation, durability, and low maintenance requirements contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of these fittings.
Maintenance and troubleshooting of a cutting ring fitting
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are critical to ensure the longevity and performance of cutting ring fittings in any high-pressure system. By periodically checking and maintaining these fittings, you can prevent leaks and system failures, which can lead to costly downtime. Below are some guidelines for maintaining and troubleshooting cutting ring fittings.
Maintenance
- Regular inspection: Schedule regular checks for wear, corrosion, and leaks. Inspect the cutting ring for correct placement and any excessive wear.
- Cleaning: Clean fittings regularly and use the right cleaning products.
- Tighten and reassemble: Tighten fittings to the recommended level.
- Replacement parts: When reassembling, check and replace the cutting ring if it's damaged. Use matching replacement parts and keep a log of sizes and types used.
Troubleshooting
- Leak detection: If a leak is detected, first identify the source. Common areas include the interface between the tube and the cutting ring or between the fitting body. Inspect for proper assembly; incorrect assembly is a common cause of leaks.
- Assessing the fitting: Check for over-tightening, which can cause the cutting ring to bite too deeply into the tubing, compromising the seal. Verify that there is no under-tightening, which can result in insufficient compression of the cutting ring and an inadequate seal.
- Tube condition: Inspect the tube for damage, such as scratches or dents, at the location of the cutting ring. Damage can prevent a proper seal and may require tube replacement. Ensure that the tube end is cut squarely and is free of burrs.
- Cutting ring examination: Look for signs of correct "bite" from the cutting ring. A visible indentation on the tube indicates a proper grip. Replace the cutting ring if it appears cracked, excessively worn, or deformed beyond its functional shape.
- Addressing system issues: Check for conditions that may cause fitting failure, such as excessive vibration, thermal cycling, or pressure spikes. Consider adding support to the tubing near the fitting to reduce stress caused by system operation.
- Preventative measures: Implement a preventative maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer's recommendations and the system's operating conditions. Train personnel on the correct installation procedures to prevent issues related to improper fitting assembly.
FAQs
What is a cutting ring fitting used for?
A cutting ring fitting creates leak-proof seals in high-pressure tubing systems.
How does a cutting ring fitting work?
A cutting ring fitting compresses a ring onto tubing, forming a tight mechanical seal.
Can cutting ring fittings be reused?
A cutting ring fitting can be used again if not damaged and properly reassembled.





