Solenoid Valves For Fuel, Oil, Gas, & Propane

Figure 1: Solenoid valve for fuel, oil, gas, and propane applications
Solenoid valves can remotely control the flow of fuel, gas, liquid propane, and other fuels in combustion systems like industrial boilers and ovens. These valves come in various types, such as 2-way and 3-way, with different operational modes. This article covers the features that make solenoid valves suitable for harsh environments, how to choose the right materials and other selection criteria.
View our online selection of solenoid valves!
What is a solenoid valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical valve used to control the flow of liquids or gasses. Due to the presence of controller circuits, these valves have near-instant reaction times, and they are commonly used in fuel injectors. Solenoid valves operate by using an electric current to generate a magnetic field, which moves a plunger to open or close the valve. This allows for precise control of fluid flow in fuel, oil, gas, and propane applications, making them useful in managing the supply and distribution of these substances.
Benefits of solenoid shut off valves
- Long service life and high reliability in harsh environments.
- Less supporting equipment and low maintenance levels result in reduced lifecycle costs.
- Less energy consumption and increased equipment uptime.
- Environment-friendly by not venting gas into the atmosphere.
- Compliance with current safety regulations.
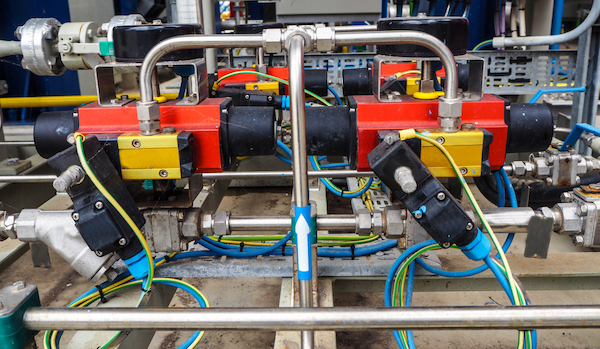
Figure 2: On-off solenoid valve for regulating fuel flow in a power plant
Selection of materials
Selecting suitable materials for the application's media is essential. For further information, refer to our solenoid valve housing material, seal material, and chemical compatibility chart.
- Common valve body material: Brass is often chosen for its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Common seal material: NBR (Nitrile Rubber) is frequently used due to its excellent resistance to oils and fuels. FKM is suitable for oil applications because it balances fluid temperature and viscosity changes with temperature.
Selection criteria
Beyond just material, consider the following factors to select the best solenoid valve for a fuel, oil, gas, or propane application:
-
Explosion-proof: The solenoid valve’s coil or enclosure must be explicitly specified to suppress any explosion originating from the valve.
- There are several standards for classifying devices for a hazardous environment like NEMA (National Electrical Equipment Manufacturers Association (USA), ATEX (Atmosphères Explosibles (EU), and IEC Ex (International Electrotechnical Commission Explosive (global)).
- Connection size: The connection sizes for solenoid valves range from 5/64 inch to 2 1/2 inch and 2 mm to 63 mm, including various specific formats such as SFB, UNF, and metric threads like M5 and M33 x 2.
- Connection type: The connection types for solenoid valves include various options such as flange, glued and welded sleeves, hose pillar, inner and outer threads in BSPT, NPT, BSPP, UNF, and metric formats, as well as plug-in, push-in, and specialized connections like Burkert cartridge and flange type 6240.
-
Normally closed vs normally open:A solenoid valve can be normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO). The common choice between the two options depends on what must happen in the case of an emergency shutoff. If flow must be blocked, an NC solenoid valve is necessary.
- A normally closed solenoid valve is closed when de-energized.
- A normally open solenoid valve is open when de-energized.
- Response time:Response time is critical for shut-off solenoid valves used with flammable fuels and oils. Direct-operated solenoid valves typically have a response time of around 30 ms, whereas indirect-operated solenoid valves can have response times of up to 1000 ms or more. Since response times vary by manufacturer and operation type, it is important to consider this factor when selecting a solenoid valve for the oil and gas industry.
- Solenoid power supply: Solenoid valves can work on AC or DC voltages. Read our article on choosing an AC or DC coil for a solenoid valve for more information.
Applications
-
Fuel systems:
- Fuel solenoid valves control the flow of fuel in engines.
- Enhance engine efficiency and reduce emissions by managing fuel delivery precisely.
-
Oil and gas industry:
- Oil solenoid valves handle the unique properties of oil in pipelines and processing facilities.
- Gas solenoid valves regulate the flow of natural gas for safe and efficient distribution.
-
Residential and commercial heating:
- Natural gas solenoid valves control gas flow to furnaces and boilers.
- Enable precise temperature regulation and energy savings.
-
Industrial applications:
- Used in processes where natural gas is a key component.
- Ensure safe and efficient operation in production environments.
-
Functionality:
- Fuel solenoids act as on/off switches for fuel flow.
- Prevent leaks and ensure safe operation of engines and equipment.
-
Overall importance:
- Provide precise control over fluid and gas flow.
- Essential for maintaining operational efficiency and safety in various settings.
FAQs
What does a fuel solenoid valve do?
The primary role of the fuel shut off valve solenoid is to regulate and oversee the fuel flow. In case of an emergency, the solenoid valve can swiftly stop the fuel supply to avert fires or other safety hazards.
Can a solenoid valve be used for gas?
Yes. A solenoid valve can be used to control gas flow. It's important to make sure the valve is compatible with the media.









