Select the right seal material for your solenoid valve

Figure 1: 2/2-way solenoid valve
Solenoid valves are often available with various sealing materials. Typical materials are NBR, EPDM, FKM (viton) and PTFE (teflon). The material choice depends strongly on the chemical properties and the temperature of the medium. The right choice is of utmost importance to guarantee a long life span and optimal valve performance. The infographic below shows the main advantages and disadvantages of the most important seal materials.
View our online selection of solenoid valves!
Select the right seal material for your solenoid valve - An infographic by Tameson!
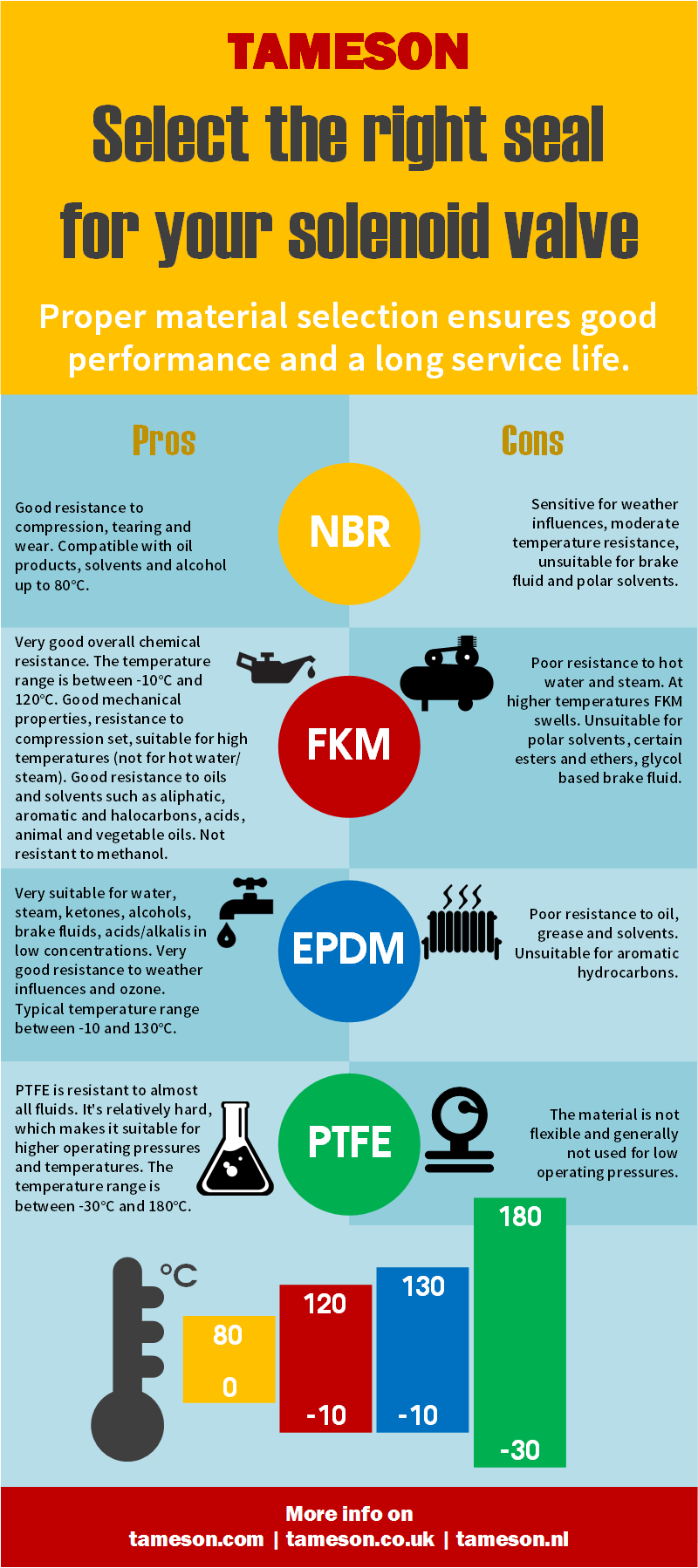
NBR
Advantages
Good resistance to compression, tearing and wear. Compatible with oil products, solvents and alcohol up to 80°C.
Disadvantages
Sensitive for weather influences, moderate temperature resistance, unsuitable for brake fluid and polar solvents.
FKM (Viton)
Advantages
Very good overall chemical resistance. The temperature range is between -10 °C and 120 °C. Good mechanical properties, resistance to compression set, suitable for high temperatures (not for hot water/steam). Good resistance to oils and solvents such as aliphatic, aromatic and halocarbons, acids, animal and vegetable oils. Not resistant to methanol.
Disadvantages
Poor resistance to hot water and steam. At higher temperatures FKM swells. Unsuitable for polar solvents, certain esters and ethers, glycol based brake fluid.
EPDM
Advantages
Very suitable for water, steam, ketones, alcohols, brake fluids, acids/alkalis in low concentrations. Very good resistance to weather influences and ozone. Typical temperature range between -10 and 130 °C.
Disadvantages
Poor resistance to oil, grease and solvents. Unsuitable for aromatic hydrocarbons.
PTFE (Teflon)
Advantages
PTFE is resistant to almost all fluids. It's relatively hard, which makes it suitable for higher operating pressures and temperatures. The temperature range is between -30 °C and 180 °C.
Disadvantages
The material is not flexible and generally not used for low operating pressures.
A more in-depth explanation of the different rubbers and a large lookup table with chemicals can be found in the article chemical resistance of materials. Read our solenoid valve overview article for more details on the design and working of solenoid valves.











