What Is Surface Acoustic Wave Technology?
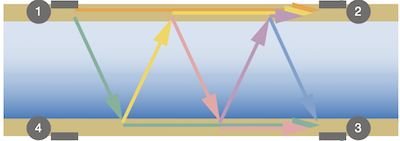
Figure 1: Surface acoustic waves split to travel across the pipe's surface and through the media flowing through the pipe.
Surface acoustic waves are particularly useful for non-invasively measuring the flow of liquids in various settings. However, the versatility of surface acoustic waves (SAWs) technology extends far beyond flow measurement; it plays an important role in ensuring cleanliness in sensitive production environments, and it enhances the functionality of everyday devices like phones and televisions. This article provides an overview of SAW technology for flow measurement and describes other surface acoustic wave applications.
View our online selection of SAW flow meters!
What is a surface acoustic wave?
A surface acoustic wave is a sound wave that travels parallel to the surface of an elastic material. As the waves travel across the surface, their displacement amplitude (i.e., a sound particle's distance from its equilibrium position) moves into the material, moving the material's particles up to a depth of approximately one wavelength. The further into the material the waves travel, the less impact they have on the material's particles.
SAWs and flow rate measurement
SAW flow meters use multiple (at least four) interdigital transducers (IDTs) that can operate as signal transmitters and receivers. These IDTs are placed on the outside of the pipe where flow measurements are taken. To take a measurement, one of the transducers sends an acoustic signal. The signal splits; part of the signal travels across the surface of the pipe directly to another transducer, which receives the signal. A portion of this signal is transmitted through the liquid to the opposite side of the tube. Upon reaching the other side, the signal splits, sending parts to the second receiver and through the liquid to continue the process.
The absolute time it takes for the wave to travel from the transmitter to the receiver is influenced by the tube diameter and the liquid type. The signal is sent in both directions, and the difference in travel time between the forward and backward directions is proportional to the flow rate. By evaluating the signals' amplitude, frequency, and runtime, the flow meter can assess the quality of the measurement and detect the presence of gas bubbles, solids, or liquid types. Learn more about how SAW flow meters work by reading our article on Burkert's 8098 flow meter.
Applications
Because SAW flow meters do not have any components that interact with the media, they are especially suitable for hygienic applications.
- Brewing and beverage industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Dairy industry
- Clean-in-place systems
SAW flow meters are used outside of specifically hygienic applications, too, simply because they are highly accurate flow meters:
- Wastewater treatment plants
- Automotive industry
- Semiconductor processing
Other SAW applications
Surface acoustic wave technology is versatile and finds applications across various fields owing to its sensitivity, precision, and reliability. Here are several surface acoustic wave devices that utilize SAW principles:
- SAW sensors: SAW sensors exploit the sensitivity of acoustic waves to environmental changes to detect physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, strain, and chemical vapor concentration. These sensors are widely used in industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications for monitoring purposes.
- SAW oscillators: In electronics, SAW oscillators are used to generate precise frequencies. These oscillators are often employed in military and space communications equipment, where stability and accuracy are critical.
- Signal processing: SAW devices can perform various signal processing functions, including modulation, convolution, and correlation. They are used in specialized applications such as spread spectrum communications and signal processing in seismology.
- SAW filters: SAW filters are essential components in telecommunications. They operate by converting electrical signals into acoustic waves, selectively filtering frequencies, and then reconverting them into electrical signals. They are found in mobile phones, TVs, radios, and other communication devices to filter out unwanted frequencies and improve signal quality.
- SAW touch screens: SAW technology is used in touch screen displays to recognize touch points. When a user touches the screen, they interrupt the acoustic waves on the surface, and the point of interruption is detected and translated into a command. This technology provides high-resolution touch screens that are durable and offer a high level of clarity.
FAQs
What is surface acoustic wave technology?
Surface acoustic wave technology uses surface acoustic waves, which propagate in a similar fashion to earthquake waves, to perform various tasks, such as monitoring systems and processing signals.
How does a surface acoustic wave sensor work?
A surface acoustic wave sensor uses transducers that transmit and receive acoustic waves. The time it takes for the waves to travel from transmitter to receiver is proportional to flow rate.





