Residual Current Circuit Breaker

Figure 1: Residual current circuit breakers
A residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) detects earth leakage in a circuit. It monitors the difference between the current flowing through the phase and neutral wires. When there is an imbalance, it trips to protect against electrical hazards. This article covers an RCCBs design, working principle, types, and advantages and disadvantages. Learn about other circuit breaker types by reading our how to identify a circuit breaker article.
What is earth leakage?
Earth leakage occurs when an electrical current leaks from an electrical appliance or circuit to an unintended path. This leakage can be unintentional (e.g., loose wires) or intentional, such as electrical equipment with small amounts of earth leakage during regular operation. In either case, it's vital to protect against shock. Improper or a lack of protection can lead to electrical accidents, fire, or damage to the equipment.
View our online selection of circuit breakers!
Residual current circuit breaker design
As seen in Figure 2, an RCCB has the following components:
- Phase wire (A): The phase wire is the live wire, or hot wire, that sends current from the power supply to the circuit.
- Breaker contacts (B): The breaker contacts are closed or open to control whether current can pass through the RCCB or not, respectively.
- Neutral wire (C): The neutral wire sends current back to the power source.
- Test button (D): The test button lets users quickly test whether the circuit breaker is functioning correctly. Pushing the button stops the flow of electricity through the breaker.
- Current limiting resistor (E): When the test button is pressed, current flows directly through the neutral wire from the phase wire. The resistor prevents the current from getting too high.
- Sensing coil (F): The sensing coil wraps around the core and determines whether there is a balance or imbalance between the phase and the neutral.
- Core (G): The core is made of ferrous material. Some core designs have a plastic cover for insulation and protection. Currents from the phase and neutral wires create opposing magnetic fields. The sensing coil monitors whether there is a difference between the two latter currents.
- Relay (H): When there is an imbalance between the phase and neutral, the relay causes the breaker contacts to open.
Read our circuit breaker overview article for more details on the working and types of circuit breakers.
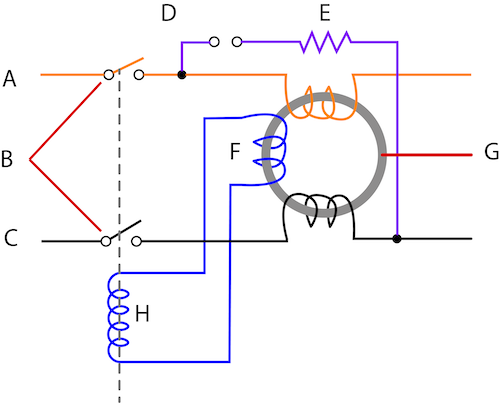
Figure 2: The components of an RCCB are phase wire (A), breaker contacts (B), neutral wire (C), test button (D), current limiting resistor (E), sensing coil (F), core (G), and relay (H).
Residual current circuit breaker working principle
When there is no fault in the circuit, the current flowing through the phase wire equals the current flowing through the neutral wire. Both wires coil around the core an equal amount, creating opposing magnetic fields. In this instance, no current flows through the sensing coil.
When there is earth leakage, current flows from the phase wire to earth. This creates an imbalance between the phase and neutral. Therefore, the two currents' magnetic fields are not in balance.
The flux between the two fields creates an electromotive force that acts on the sensing coil. This creates a current flow through the sensing coil and relay. The relay forces the breaker contacts to open, halting current flow through the circuit breaker.
Types of residual current circuit breakers
Another name for RCCB is residual current device. Therefore, circuit breakers with either name operate similarly. This section covers some specific types of RCCBs that operate under specific conditions or in specific applications.
Residual current circuit breakers with overcurrent protection

Figure 3: A residual current circuit breaker with overcurrent protection
A residual current circuit breaker with overload protection combines the functions of an RCCB and an overcurrent protection device in a single unit. It interrupts the circuit if it detects either earth leakage or overcurrent. The overcurrent protection mechanism, consisting of a thermal-magnetic tripping unit, monitors the current flowing in the circuit and trips if it exceeds the rated current, preventing damage from overloading.
Ground fault circuit interrupters

Figure 4: A ground fault circuit interrupter
A ground fault circuit interrupter detects earth leakage in low-voltage electrical systems. The circuit interrupters can be installed in circuit outlets to protect against electrical shock in wet areas, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Portable ground fault circuit interrupters are also available to provide protection although the circuit interrupter is not installed to the circuit. These circuit interrupters detect and quickly trip or shut off a circuit if there is a difference in the amount of electricity flowing in and out, even with as little as 4-5 milliamps.
Ground fault relays
Ground fault relays are used in industrial systems to protect against earth faults. They monitor the neutral conductor current and trip a separate breaker if a fault exceeds 5 mA. These relays protect against earth faults and work in conjunction with a breaker for comprehensive protection. They are used in high-current applications where more than standard protection is needed.
Residual current circuit breaker advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- No connection to earth: Unlike an earth leakage circuit breaker, an RCCB can detect earth leakage without needing an earth wire.
- Test button: The test button on an RCCB makes it easy to test whether or not the circuit breaker is functioning correctly.
- Voltage variation: Rising and falling of voltage in the current can be detected by an RCCB.
Disadvantages
- Other fault types: Basic RCCBs cannot detect overcurrent or short circuits. The former requires a residual current circuit breaker with overload protection. The latter requires the RCCB to be used with a miniature circuit breaker.
- Phase to earth only: The RCCB only protects against electric shock if the current flows from phase to earth. If the current flows from phase to phase (through an individual) or from phase to neutral, the RCCB does not protect against shock.
- Improper tripping: When electric loads suddenly change, especially in older appliances, some of the current may go to earth. This can lead to the RCCB tripping when there is no risk of electrical shock.
Read our articles on miniature circuit breakers,smart circuit breakers and earth leakage circuit breakers for more details on the features of various circuit breaker types.
FAQs
Why are residual current circuit breakers used?
Residual current circuit breakers are used to protect against electrical shocks in the case of the phase current going to earth.
Residual current device vs circuit breaker
A residual current device protects against electric shocks whereas a circuit breaker protects against electrical hazards caused by faulty circuits.





