Pressure Transducer Working Principle

Figure 1: Pressure transducer
A pressure transducer converts pressure into an electrical output signal. The electrical signal can be digital or analog and is used by other devices such as controllers, alarms, and other closed-loop systems. Pressure transducers are used widely in various residential and commercial applications like HVAC, pumps, vehicles, aircraft, etc., where pressure measurement is required. They are also referred to as pressure sensors or pressure transmitters. These devices are crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in systems by providing accurate and real-time pressure data.
Table of contents
- Pressure transducer working principle
- Types of pressure transducers
- Selection criteria
- Common applications
- How to test a pressure transducer with a multimeter
- FAQ
Pressure transducer working principle
A pressure transducer consists of a pressure-sensitive element, such as a diaphragm, with a constant area. The fluid pressure causes the diaphragm to deflect. The pressure transducer also consists of a transduction element. This transduction element converts the deflection sensed by the diaphragm into an electrical output signal. This signal will increase or decrease proportionally to the pressure change. Therefore, device calibration is critical to ensure that the pressure is within the range of the specifications.
Pressure transducers require a power supply to produce electrical signals. The signal is commonly 4-20 mA or 0-10 V DC. Some systems may also use a combination of AC and DC power. The 4-20 mA signal is a widely used standard in the industry. It uses a 2-wire configuration, while DC voltage output uses a 3-wire configuration. The 4-20 mA signal can be used over long distances and is less sensitive to interference than a DC signal.
A pressure transducer should not be confused with a pressure switch. A pressure switch is a device that operates an electrical contact when a preset fluid pressure is reached. Read our pressure switch technical article to learn more about them.
Types of pressure transducers
There are different pressure transducer types based on their measurement technology. The main types are outlined below:
Strain gauge pressure transducer
These transducers are suitable for measuring extraordinarily high and low and differential pressures. Differential pressure is the difference in pressure between any two given points. The transducer contains a sensing element, a diaphragm. Any deformation of the diaphragm will cause a change in the resistance of the strain gauges. Typically, four gauges are used in a Wheatstone bridge to maximize the transducer's sensitivity. This resistance change is converted into a usable output signal.
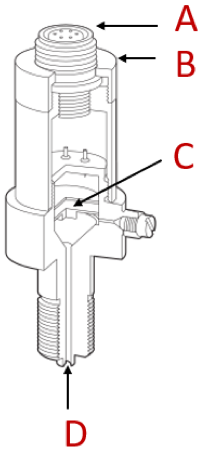
Figure 2: Strain gauge pressure transducer components: connector (A), housing (B), strain gauge (C), & pressure inlet (D)
Capacitance pressure transducer
Capacitance pressure transducers measure pressure by detecting the changes in electrical capacitance due to the movement of the diaphragm. It has two capacitor plates, a diaphragm, and an electrode fixed to an unpressurized surface. These plates are at a certain distance from each other, and the change in pressure will widen or narrow the gap between these plates. This change in capacitance is converted into a usable signal. Depending upon the application, this transducer can measure either absolute, gauge, or differential pressure.
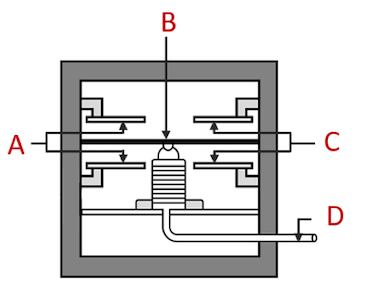
Figure 3: Capacitance pressure transducer components: insulated standoffs (A), diaphragm (B), capacitor plates (C), & pressure port (D)
Potentiometric pressure transducer
This type of transducer consists of a precision potentiometer. The potentiometer consists of a wiper connected to the pressure-sensitive element, such as a diaphragm. The deflection on this element changes the position of the wiper. The resistance value changes between the wiper and one end of the potentiometer. This value is the measure of the pressure applied.
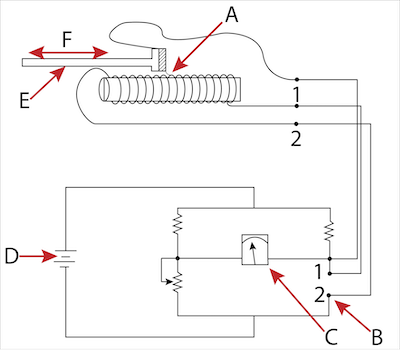
Figure 4: Potentiometric pressure transducer components: wiper (A), resistance-measuring bridge circuit (B), measurement proportional to pressure (C), bridge power supply (D), movable arm of pressure element (E), & displacement (F)
Resonant wire pressure transducer
Resonant wire pressure transducers have a vibrating wire located in a diaphragm. The electronic oscillator keeps the wire vibrating. As the pressure changes in the diaphragm, the tension of the wire and the resonant frequency change. This frequency can be sensed by digital counter circuits and converted into an electrical signal.
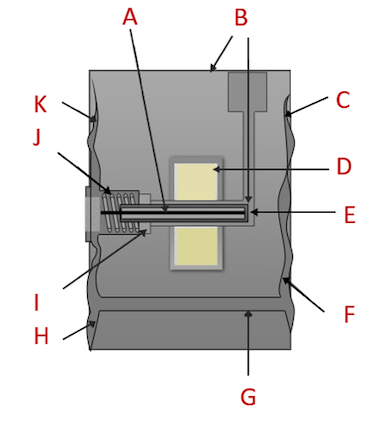
Figure 5: Resonant wire pressure transducer components: resonant wire (A), to oscillator circuit (B), high-side backup plate (C), magnet (D), metal tube (E), high-pressure diaphragm (F), fluid transfer port (G), low-pressure diaphragm (H), electrical insulator (I), preload spring (J), & low-side backup plate (K)
Inductive pressure transducer
Inductive pressure transducers operate using the principle of electromagnetic induction. The transducer has a diaphragm connected to a ferromagnetic core. The slight deflection of the diaphragm causes linear movement in the ferromagnetic core, which induces a current. The movement of the core due to the change of pressure varies the induced current. This change in current is converted into a usable signal.
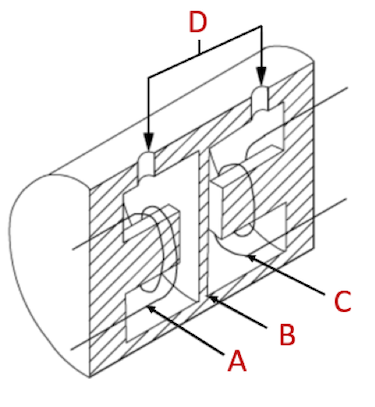
Figure 6: Inductive pressure transducer components: coil (A, C), diaphragm (B), & pressure (D)
Piezoelectric pressure transducer
When pressure is applied, the piezoelectric pressure transducers use quartz crystal or ceramic material to generate an electric charge. This electric charge, measured as a voltage, is proportional to the change in pressure. This transducer is very sensitive and extremely fast in response.
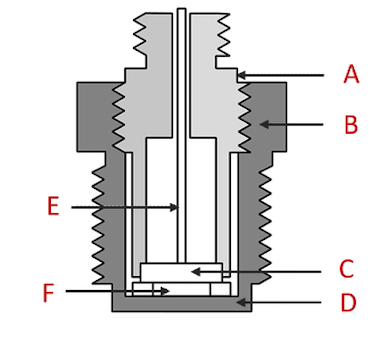
Figure 7: Sectional view of piezoelectric pressure transducer components: Lead wire (A), disc (B), nut (C), housing (D), crystal (E), and diaphragm (F).
Selection criteria
When selecting a pressure transducer, consider the following parameters:
-
Type of media: The type of media should be compatible with the material of the transducer. Some commonly used media types include:
- Hydraulic oil
- Heating oil
- Petrol/gasoline
- Adhesives
- Compressed air
- Gasses
- Water
- Housing and seal material: The housing and seal material of the transducer should be chemically compatible with the application media. Stainless steel is the most commonly used housing material. It provides high material strength and greater compatibility with neutral and corrosive fluids. Common seal materials are Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), Viton (FKM), and elastomers.
- Temperature: Extreme temperature may limit the functionality of the transducer. Therefore, ensure the pressure transducer is within the application’s temperature range.
- Pressure: The transducer must be able to withstand the operating pressure range as well as overpressure for the application. Specially designed high-pressure transducers are available for extreme-pressure applications.
- Type of transducer: Capacitance and resonant wire pressure transducers are suitable for absolute and gauge pressure. A strain gauge transducer is suitable to use as a differential pressure transducer.
- Hysteresis: Hysteresis is the ability of the pressure transducer to produce the same output when the same increasing and decreasing pressure is consecutively applied. For low-hysteresis, a capacitive pressure transducer is desired.
- Repeatability: Repeatability is the ability of the pressure transducer to produce the same output at the same pressure. It generally ranges from 0.5% to 0.05%. The selection of a transducer will depend upon the accuracy desired by the application.
- Approvals: Pressure transducers may require approvals or certifications, such as ATEX and IECEx, to operate in specific environmental conditions.
Common applications
Pressure transducers are used in a wide range of residential and commercial applications that require pressure measurement. Therefore, depending on the media, there are air pressure transducers, liquid pressure transducers, and gas pressure transducers. Some typical electronic pressure transducer applications include:
- Monitoring the brake and fuel pressure in vehicles.
- Monitoring liquid levels in a HVAC system.
- Sensing the liquid level for well and pump stations.
- Altitude sensing for aircraft and satellites.
- Monitoring liquid and gas levels on various medical devices.
How to test a pressure transducer with a multimeter
Knowing how to test a 4-20mA pressure transducer is essential to ensure accurate and reliable performance in a system. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to test a pressure transducer, specifically focusing on the 4-20mA output signal.
Tools required
- Multimeter
- Power supply (typically 24V DC)
- Pressure source (e.g., hand pump or pressure calibrator)
- Wiring connectors
Step-by-step guide
- Safety first:
- Ensure that the system is depressurized and safe to work on.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Initial inspection:
- Visually inspect the pressure transducer for any signs of physical damage or wear.
- Check the wiring and connectors for any loose or damaged connections.
- Set up the multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure current (mA).
- Ensure the multimeter is capable of measuring the 4-20mA range.
- Connect the power supply:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to the positive input of the pressure transducer.
- Connect the negative terminal of the power supply to the common ground.
- Connect the multimeter:
- Connect the multimeter in series with the pressure transducer. This means connecting one lead of the multimeter to the negative terminal of the power supply and the other lead to the negative input of the pressure transducer.
- Apply pressure:
- Gradually apply pressure to the transducer using a pressure source.
- Monitor the pressure applied using a calibrated gauge or the pressure source’s display.
- Read the multimeter:
- Observe the current reading on the multimeter. A properly functioning 4-20mA pressure transducer will output 4mA at zero pressure and 20mA at its maximum rated pressure.
- For intermediate pressures, the current should proportionally vary between 4mA and 20mA.
- The exact output values corresponding to different pressure readings will be specified in the manufacturer’s datasheet. Refer to the datasheet to verify if the transducer is working as per the specifications.
- Verify output:
- Compare the multimeter readings with the expected values based on the applied pressure. For example, at 50% of the transducer’s full-scale pressure, the output should be approximately 12mA.
- If the readings are not within the expected range, there may be an issue with the transducer or the setup.
- 4-20mA pressure transducer troubleshooting:
- If the transducer does not output the correct current, check the power supply voltage to ensure it is within the specified range.
- Verify all connections are secure and correct.
- If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or consider replacing the transducer.
FAQ
What is a pressure transducer and how does it work?
A pressure to current transducer converts pressure into an electrical signal that can be read by an instrument. It senses the pressure and generates a signal proportional to the pressure applied to it.
How do you test a pressure transducer?
Apply a known pressure to a pressure transducer and measure the output signal to test it. To verify accuracy, compare the output signal to the expected value and calibrate if necessary.
What is the difference between a pressure sensor and pressure transducer?
A pressure transducer transforms pressure into an electrical signal that can be read by an instrument or control system, as opposed to a pressure sensor, which detects pressure and produces a signal.
What is the difference between a pressure transducer and pressure transmitter?
These two terms are often used interchangeably. However, a pressure transducer transforms pressure into an electrical signal, and a pressure transmitter can also amplify, modify and send that signal.
What does a pressure transducer measure?
A pressure transducer measures the force exerted on it per unit area and converts it into an electrical output signal that can be read by an instrument or control system.
How to use a pressure transducer?
To use a pressure transducer, determine the type of fluid or gas, select the appropriate transducer, install it, and calibrate it for accurate readings.
How does a differential pressure transducer work?
This type of transducer measures the difference in pressure between two points and converts it into an electrical signal used in flow measurement and liquid level detection.




