Power Converter

Figure 1: A power converter
A power converter is an electrical circuit that converts the electrical energy from one form into another, usually utilizing a high-frequency switching action. This conversion can be from direct current to alternating current or alternating current to direct current to increase or decrease the voltage or change the polarity. Also, the converter acts as a link between the power source and the power supply output. It works to process and control the flow of electric energy by supplying currents and voltage in the form needed for the end-user loads. Converters are available in the form of a simple transformer or maybe more complex, depending on the application. This article discusses the various types of power converters.
Table of contents
- Alternating Current versus Direct Current
- Types of power converters
- AC to DC converters
- DC to AC converters
- DC to DC converters
- AC to AC converters
- FAQs
View our online selection of transformers!
Alternating current versus direct current
Alternating Current (AC) refers to the electric current that periodically reverses its direction. This is the type of current that powers your home or business. It is the outlet that the devices are plugged into. Alternator devices produce alternating currents.
In contrast, Direct Current (DC) flows only in one direction. In a direct current, the electrons move from a region of negative charge to a region of positive charge without changing their direction. The most frequent power source for DC is batteries, which power cell phones, automobiles, and flashlights.
Types of power converters
The type of conversion categorizes power converters. They generally fall into four categories:
- AC to DC converters: AC to DC convertersconvert alternating current to direct current using a rectifier.
- DC to AC converters: DC to AC converters take direct current and convert it to an alternating current of the desired voltage and frequency. These are inverters.
- DC to DC converters: These converters convert either a constant current to a variable or a constant direct current. These devices are also called choppers.
- AC to AC converters: AC to AC converters are often called cycloconverter or matrix converters. These devices convert an alternating current of a specific frequency or voltage from a line alternating current source to a different alternating voltage.
AC to DC converters
One of the essential elements in electrical conversion is going from alternating currents to direct currents. The applications, known as AC - DC converters, convert the alternating current to a direct, one-directional current. Transformers adjust the AC source, reducing the voltage for a better operational range for the DC supply. This conversion from alternating current to direct current has become significant during recent years because of the amount of technology in homes that require DC to charge them.
This converting alternating current to direct current is rectification, and the converter is called a rectifier. Also, a series of diodes convert the AC supply into DC. This transforms the sinusoidal AC wave into a series of positive peaks. A transformer adjusts the current from the source to a more manageable voltage for use at the direct current supply.
AC to DC conversion process
The alternating current supply from the step-down transformer is converted to the DC at the load end connection using the rectifier. Not all rectifiers are alike, and the different types refer to their functions, namely the half-wave, full-wave, and bridge rectifiers.
A half-wave rectifier or a full-wave rectifier can be used to convert an alternating voltage to DC voltage. An alternating voltage (labeled A) is applied to the primary windings of the step-down transformer (Figure 2 labeled B). A corresponding voltage is induced at the secondary windings. Frequently, transformers decrease the voltage for use in equipment that needs power at a lower level. When there is an available 230 volts of alternating current, the step-down transformer can convert it into 12 volts.
The diode (Figure 2 labeled D) becomes forward biased (ON state) and conducts current initiating current flow through the load resistor (Figure 2 labeled R). A diode allows the current to flow in one direction. During the negative cycle of the input voltage, a corresponding negative voltage is induced in the secondary side, and the diode doesn’t conduct. Hence, there is no flow through the output resistor during the negative cycle of the input voltage as the diode behaves as an open circuit. Therefore the output gives only alternate positive cycles.
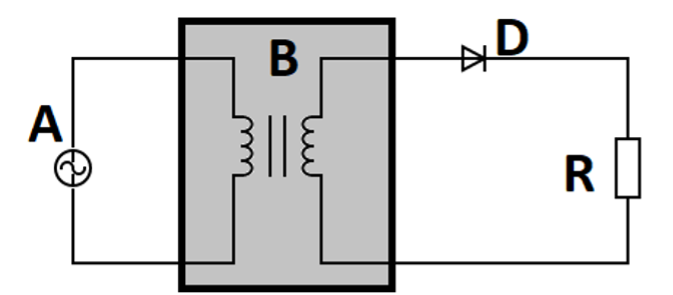
Figure 2: Half wave rectifier circuit
For practical applications, a capacitor is connected to the output in parallel with the resistor (See Figure 3). The capacitor acts as a filter to smooth out the pulsating output voltage to the appropriate DC level. Read our article on AC to DC transformers for more details on the rectification process.
A voltage regulator integrated circuit regulates the output voltage to the fixed desired value. This is the final step in converting alternating current to direct current in the output voltage at the desired volume.
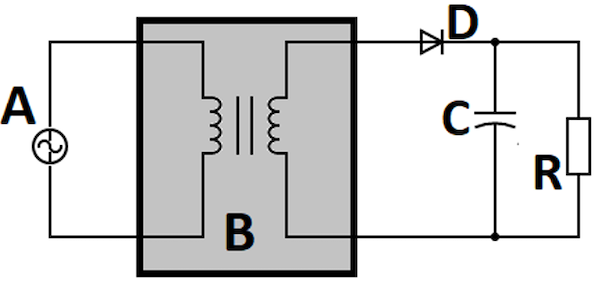
Figure 3: Half wave rectifier with capacitor filter
Benefits of an AC-DC Converter
There are three significant benefits to an alternating current to a direct current converter.
- Compact: Devices that require AC-DC converters utilize the smallest possible sizes to convert the current efficiently, offering smaller devices. In an industrial setting, AC-DC converters are lightweight and easy to install.
- Energy Efficient: AC-DC converters eliminate the need for additional inverters and converters because they perform efficiently and reduce equipment failure.
- Less Expensive: Converting the current to a lower voltage saves users money on energy usage.
Applications
AC to DC converters are used in most household appliances, such as refrigerators, computers, televisions, and chargers for handheld electronics such as cell phones or tablets. Also, they play an essential role in medical equipment, the aerospace industry, and transportation systems. Household and industrial use rely heavily on AC-DC converters.
DC to AC converters
Perhaps a less frequent conversion is Direct Current to Alternating Current. An inverter converts a direct, one-directional current into an alternating, reversing current. DC to AC converters can be designed in multiple ways. One common method is to employ an oscillator and a step-up transformer.
An oscillator is an electronic circuit employing transistors and other semiconductor devices used to generate an alternating signal from a small DC voltage source. The AC signal can then be stepped up using a step-up transformer to the desired voltage magnitude.
Limitations of DC to AC conversion
There are a couple of limitations in converting direct current to alternating current.
- Transistor usage reduces circuit efficiency.
- Switching transistors can result in cross-over distortion but can be reduced by blasing diodes.
Applications
The primary use of direct current to alternating current charges vehicle batteries. But this current can also drive low-powered AC motors and solar-powered systems.

Figure 4: DC to AC power converter used in cars
DC to DC converters
Some applications involve converting one source of direct current to another voltage of direct current. A DC to DC converter draws a DC input voltage at its input and delivers a different DC voltage. The output DC voltage can be lower or higher than the input voltage applied. DC to DC converters are available as individual integrated circuits (ICs), requiring very few additional components for their operation.
Applications
Cell phones and laptops receive battery power but contain sub-circuits that regulate the voltage requirement different from the batteries.
AC to AC converters
AC to AC converters refers to a device that converts an alternating current waveform from one form into another. The output voltage and frequency are managed according to the device's usage and requirements. One way of achieving this is to use special semiconductor devices (like thyristors) to switch on and off the input voltage supply in a circuit so that the average voltage at the output can be varied according to the application.
Applications
Simple applications can control motor speeds, dimming lamps, or heat control.
FAQs
What is a power converter used for?
Power converters are essential in taking the alternating electrical current in our homes and converting it to direct current used to power appliances, charge batteries, and operate office equipment.
Do phone chargers need a converter?
Most mobile devices that require a battery charger do not need a separate converter.
How are converters and inverters different?
A converter converts AC to DC, while an inverter converts direct current to alternating current.











