What Is a Latching Solenoid Valve

Figure 1: Latching solenoid valve
Latching solenoid valves hold their open or closed position without continuous power. These valves use permanent magnets and electromagnetic coils to switch between open and closed states. They consume significantly less energy than conventional spring-return solenoids, making them ideal for battery-powered systems and remote control applications. This article explores the working and features of latching solenoid valves.
Table of contents
- Applications of latching solenoid valves
- What are the main components of a latching solenoid valve?
- Latching solenoid valve design types
- Residual magnet latching solenoid valve
- Disadvantage
- FAQs
View our online selection of solenoid valves and buy one today!
Applications of latching solenoid valves
Latching solenoid valves are mainly used when power efficiency or limited power availability is a top priority. They are commonly used in irrigation controllers and low-power systems, such as battery- or solar-powered devices. Common applications are:
- Door locks
- Industrial instrumentation
- Battery-operated fluid systems
- Air conditioning units
- Industrial cleaning equipment
What are the main components of a latching solenoid valve?
Figure 2 shows the main components of a latching solenoid valve. Figure 3 demonstrates how the valve works:
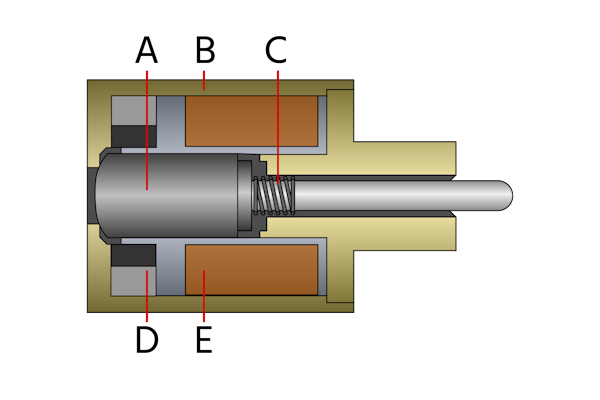
Figure 2: Components of a latching solenoid valve. Armature (A), housing (B), spring (C), permanent magnet (D), and solenoid coil (E).
- Solenoid coil (E): When the electric current is applied, the solenoid coil generates a magnetic field. The polarity of this field determines whether it reinforces or opposes the permanent magnet's field.
- Armature/Plunger (A): The armature moves when the combined magnetic forces of the coil and permanent magnet overcome the spring force and system pressure.
- Permanent magnets (D): Once the plunger is in the desired position (either open or closed), permanent magnets maintain this position even after the initial electrical power is removed. They provide the necessary magnetic force to hold the plunger in place without continuous power.
- Spring (C): When a reverse-polarity pulse is applied to the coil, it creates a magnetic field that opposes the permanent magnet's field. This reduces the total magnetic holding force, allowing the spring to return the armature to its original position.
-
Valve housing (B):The valve body houses all components under pressure and connects to the fluid circuit being controlled. It is constructed from strong and durable materials such as brass, stainless steel, and plastic.
- The housing and seal materials are chosen based on the fluid type, pressure rating, and environmental conditions. Read our articles on solenoid valve housing and seal materials for more details.
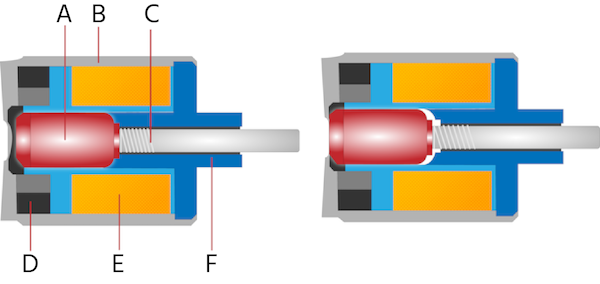
Figure 3: The permanent magnet is not strong enough to move the armature (E), but when the solenoid is energized, the combination moves the armature (F). The permanent magnet is strong enough to hold the armature in place (G) until a reverse polarity cancels the permanent magnet's field (H) and the armature returns to its default position.
Disadvantage
Latching solenoids are not suitable for failsafe applications or safety valves during power outages. They require batteries or a UPS to maintain operation during power outages. Also, consider installing an additional valve alongside the primary latching solenoid valve. The secondary valve serves as a backup, maintaining fluid control even if the primary valve fails or loses power.
FAQs
Where are latching solenoid valves used?
Latching solenoid valves are used in portable, battery-operated home appliances and HVAC systems.
What factors should I consider before operating a DC latching solenoid valve?
Applying the correct current is vital for the proper operation of latching solenoid valves. Insufficient current can prevent the whole operation, while excessive voltage can cause overheating and premature wear.
How can you know if your magnetic latching solenoid valve is malfunctioning?
Check if the valve fails to open or close, remains partially open, generates a buzzing noise, or has a leakage problem. For more details, refer to the manufacturer's guide.
How does a battery-operated solenoid valve control water flow?
A battery-operated solenoid valve uses electrical energy from a battery to open or close, controlling water flow. It's ideal for remote or portable applications where power access is limited.













