Check Valves For Pneumatic Systems

Figure 1: Aluminum check valve for pneumatic applications
Check valves prevent the backflow of air in pneumatic systems, which protects compressors and other equipment from potential damage caused by reverse flow. This article discusses the features of air check valves, their typical applications, and standard troubleshooting techniques.
Table of contents
- How to select pneumatic check valves
- Applications of pneumatic check valves
- Troubleshooting pneumatic check valves
- FAQs
View our online selection of pneumatic check valves!
How to select pneumatic check valves
Connection size and type
Match the connection size of the check valve to the existing piping in the system. Threaded (BSP, metric) and push-in connections are commonly used in pneumatic applications.
- Threaded connections have high vibration resistance compared to push-in fittings. They are more ideal for permanent installations.
- Push-in connections allow for rapid installation without the need for tools. They are easy to disconnect, making them ideal for systems that require regular maintenance.
Check valve features
Flow to the thread
A "flow to thread" check valve allows fluid flow from the push-in connection (hose side) toward the threaded connection. Flow to the thread connection is suitable for applications where air needs to be delivered to a device or system connected via a threaded port. The connection is typically used in pneumatic tools, air supply lines, and systems where the air source is flexible (hose) and the destination is fixed (threaded).
Flow from the thread
A "flow from thread" check valve allows fluid flow from the threaded connection toward the push-in connection (hose side). This setup is used to direct air from a fixed component, such as a compressor or a fixed pipeline, to a flexible hose in pneumatic distribution systems. An arrow on the check valve body indicates the direction of flow.
Auto shut-off
The auto shut-off feature ensures that the valve automatically closes and stops the flow when the hose is removed. In systems where tools or equipment need to be frequently changed or moved, auto shut-off fittings allow for quick disconnection without manual intervention. They are commonly used in:
- Portable equipment
- Systems that require regular maintenance
- Pneumatic distribution systems where multiple lines are connected to a central air supply
- Manufacturing or assembly lines where pneumatic tools are frequently swapped
Minimum pressure difference
The minimum pressure difference is the smallest pressure differential needed to open a check valve. In delicate pneumatic control systems or precision instruments, selecting a check valve with a zero bar cracking pressure is ideal, as it opens with minimal resistance.
Read our check valve overview article for more information on the design and working of check valves.
Applications of pneumatic check valves
Pneumatic check valves are widely used across various industries and applications where maintaining consistent air pressure and preventing reverse flow are crucial.
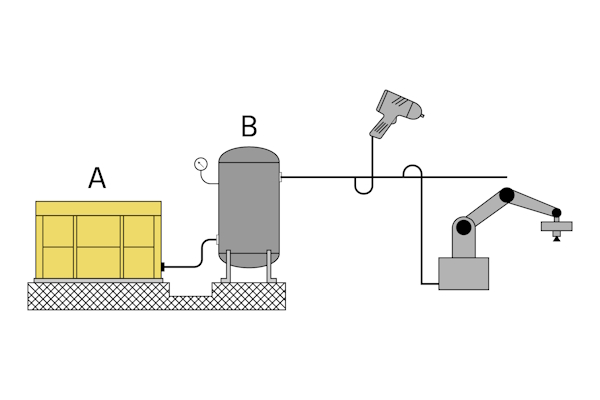
Figure 2: The workflow from air generation to distribution: air compressor (A), receiver tank (B), and a pipeline network with multiple outlets supplying pneumatic tools, machinery, and robotic systems. Check valves are installed between the compressor and the tank, as well as at key distribution points (not shown in the image).
Air compressors
Check valves for compressed air are installed between the compressor and the storage tank. They prevent compressed air from flowing back into the compressor when it is turned off or not in operation. This prevents pressure loss and ensures that the air supply remains available for use, even when the compressor is off.
Pneumatic tools
Many pneumatic tools, such as air hammers or impact wrenches, utilize check valves to maintain consistent air pressure within the tool. They ensure a steady air supply while preventing backflow when the unit is not in use. This enhances tool efficiency, prolongs lifespan, and provides smoother operation.
Pneumatic control systems
Check valves maintain pressure differentials in complex pneumatic control systems, ensuring air flows through specific circuits only when required. This keeps the system pressurized and prevents air loss from sensitive areas.
Multi-source pneumatic systems
In systems with multiple air sources, check valves prevent air from flowing backward into a non-operating source. They ensure a continuous air supply and prevent the failure of one source from affecting the entire system.
Vacuum systems
In pneumatic vacuum systems, check valves prevent the loss of vacuum integrity by stopping any backflow of air. They maintain necessary vacuum pressure, ensuring efficient operation of vacuum-powered tools or systems.
Sequential operation in pneumatic circuits
Check valves facilitate sequential operation in pneumatic circuits, ensuring processes occur only when the required pressure is available and preventing premature backward air movement. This enables precise control of automation processes, ensuring that operations happen in the correct order.
Airlock systems
In manufacturing environments, check valves are used to create airlock systems by forming chambers that prevent air from escaping or flowing backward. This maintains a controlled environment with consistent pressure for specific tasks, such as material handling or packaging processes.
Troubleshooting pneumatic check valves
Symptoms of a bad check valve
- Air leakage: Continuous air escaping from the unloader or pressure release valve.
- Pressure loss: Difficulty maintaining pressure, especially noticeable overnight
- Starting issues: The compressor struggles to start without a load.
- Unusual noises: Excessive noise during operation, indicating potential valve issues
How to fix common check valve failures
-
Debris contamination:Particles obstruct the valve, preventing it from sealing correctly.
- Place a filter upstream to remove particulates from the air supply, preventing debris from reaching the check valve. Read our FRL overview article for more details on how a pneumatic filter, regulator, and lubricator unit works.
-
Seal wear or damage:Worn or damaged seals lead to air leaks.
- Schedule routine inspections to check for seal wear and replace seals as needed.
-
Spring failure:A broken or weakened spring prevents the spring from closing fully.
- Inspect springs during maintenance checks and replace any that show signs of wear or weakness.
- Ensure the system operates within the valve's pressure limits to avoid overstressing the spring.
-
Corrosion:Moisture or corrosive substances degrade valve materials.
- Use corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or brass, for valves in corrosive environments.
-
Improper installation:Over-tightening or misalignment introduces stress.
- Follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines. Ensure the correct alignment of valves and avoid over-tightening.
-
Mechanical fatigue:Repeated cycling or excessive pressure causes wear and tear.
- Use a pressure regulator to maintain consistent pressure and avoid exceeding the valve's rated limits.
- Securely mount valves and use vibration dampeners to minimize mechanical fatigue caused by vibrations.
How to troubleshoot a faulty check valve in a pneumatic system
-
Visual inspection:
- Inspect the valve body and connections for visible damage, wear, or corrosion.
- Pay attention to threads and connections for signs of stress or over-tightening.
-
Functional testing:
- Test the valve by blowing air through it in the reverse direction; it should not allow air to pass. If air passes, the valve is not sealing properly.
- After ensuring the valve is installed correctly, monitor the system's pressure over time. Sudden pressure drops can indicate that the valve is not sealing correctly, allowing air to leak back through the valve.
-
Leak detection:
- Use soapy water to identify leaks. Apply the solution to potential leak points and look for bubbles.
- Focus on the check valve, pressure switch, and connections. Pneumatic connections, such as fittings and joints, are common leak points due to wear or improper sealing.
-
Component inspection:
- Remove and inspect internal components for debris or damage.
- Inspect the seal, o-rings, and spring for any cracks or wear. Replace if necessary.
-
System-specific troubleshooting:
- Compressor check valve leaks: If air leaks from the pressure release valve or the compressor cycles too often, inspect for a damaged seal washer or weakened spring that may be allowing tank air to flow back into the compressor.
- Pressure loss in compressor systems: If the system cannot hold pressure, perform leak detection, then inspect the check valve and pressure switch for faults, adjusting or replacing them as needed.
-
Resolution:
- Clean, repair, or replace defective parts.
- For recurring failures, upgrade to more durable materials (e.g., stainless steel).
- Reassemble, reinstall, and retest to confirm proper sealing and operation.
FAQs
Where is a check valve located in an air compressor?
The check valve is located at the air tank's inlet, where it connects the discharge line from the compressor pump, allowing air in but preventing backflow.
What is the function of the air tank check valve in a compressor system?
The air tank check valve allows air to enter the tank while preventing it from flowing back into the compressor.
Can an air check valve be submerged?
Yes, however, the longevity of a submerged check valve depends on the materials used in its construction.
What are the common symptoms of a bad air pump check valve in a compressor system?
Common symptoms include continuous air leakage from the pressure release valve and frequent compressor cycling due to pressure loss.






