Understanding Threaded Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings

Figure 1: Stainless steel threaded fittings from left to right: double nipple, tee, elbow, and reducing nipple.
Threaded stainless steel pipe fittings create secure and reliable connections in various piping systems. They are used for their corrosion resistance, strength, and versatility, which make them ideal for use in challenging environments. These fittings are typically used in petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing industries. The variety of fittings available (e.g., elbows, tees, reducing nipples, and swivel joints) allows customized solutions to meet specific industry demands. This article covers the different types of stainless steel threaded fittings, their applications, and considerations for selecting the right one for a project's needs.
Table of contents
- Overview of stainless steel threaded fittings
- Types of stainless steel threaded fittings
- Selection criteria
- FAQs
View our online selection of stainless steel threaded fittings!
Overview of stainless steel threaded fittings
Threaded fittings are essential for connecting pipes in various industrial applications. Their primary function is to provide a consistent and leak-proof pathway for transporting liquids or gasses under varying pressure and temperature settings. These fittings are available in different thread types, with stainless steel npt pipe fittings being the most commonly used standard in the U.S. industry due to its tapered threads, which promote tighter seals. The threading ensures compatibility and ease in installation and disassembly, reducing downtime during maintenance.
Types of threads
Several threading standards exist, such as the Unified National Thread (UN/UNF), British Standard Pipe (BSP), and Metric Thread (ISO 68-1).ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 governs NPT threads, ensuring pitch, diameter, and engagement length standardization. The choice of threading often influences the connection's performance, with tapered threads offering better sealing capabilities than parallel threads.
Table 1: NPT, BSPP/BSPT, and metric thread standards
| NPT | BSPP/BSPT | Metric |
|---|---|---|
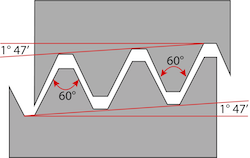 |
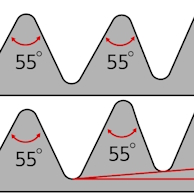 |
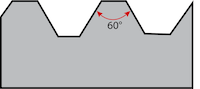 |
Importance in various industries
Due to their corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel threaded fittings find applications across industries like petrochemicals, food production, and HVAC systems. They uphold safety and efficiency standards and are used in essential tasks such as fire protection systems, cooling installations, and chemical transport. Engineers and technicians must understand the threading and standard specifications to ensure these fittings meet stringent industry requirements.
Stainless steel vs other materials
Stainless steel threaded fittings have unique characteristics compared to those made from brass or PVC. Stainless steel is very strong and durable, which makes it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. It also resists corrosion and works well in harsh or corrosive conditions. Unlike brass, which can weaken over time, stainless steel stays strong. PVC can degrade or crack when sunlight or certain chemicals are exposed, but stainless steel remains stable. These features make stainless steel fittings a reliable choice for industries like petrochemicals, food processing, and HVAC systems, where secure and leak-proof connections are important.
Types of stainless steel threaded fittings
Stainless steel threaded fittings include many structures to suit different plumbing and flow system needs. Table 2 describes the most notable types.
Table 2: Stainless steel threaded fittings
| Stainless steel fitting type | Description | Max pressure at 20 °C [68 °F] | Notes |
| Stainless steel threaded pipe fittings | General fittings with typically two male threads for extending or connecting pipes with female threads. Sometimes one male thread and one end for welding. | 16 or 20 bar (232 or 290 psi) | Can be straight or elbow shaped |
| Stainless steel tee fittings | Used for diverting flow from the main pipeline to a branch line in a T-shape. | 10 - 475 bar (145 - 6900 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel cross fittings | Similar to tees, but with an additional opening for multiple flow directions. | 16 bar (232 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel NPT threaded fittings | Fittings with National Pipe Taper threads. | - | There are several types of fittings with NPT connections including angled, double nipple, end cap, reducing nipple, socket, and tee. |
| Stainless steel reducer nipple | Used to connect two pipes of different diameters. | 40 to 640 bar (580 to 1184 psi) | There are reducing adapters (male thread is smaller than the female thread) and reducing rings (male thread is larger than the female thread). |
| Stainless steel double nipple fittings | Double-ended male threaded fittings for connecting pipes. | 16 to 475 bar (232 to 6890 psi) | The ends can be the same or different sizes. |
| Stainless steel socket fittings | A socket is a female-threaded short pipe used to connect two male-threaded pipes or components. | 16 to 575 bar (232 to 8340 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel end cap and plug fittings | Used to close the end of a pipe or fitting. | 16 to 575 bar (232 to 8340 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel threaded extensions | Used to extend the length of threaded pipe connections. | 40 or 345 bar (580 to 5000 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel y-piece fittings | Y-shaped fittings for splitting flow into two directions. | 16 bar (232 psi) | - |
| Stainless steel angled fittings | Fittings designed to change the direction of flow at an angle. 45° or 90° | 45° - 16 to 350 bar (232 to 5080 psi) 90° - 10 to 575 bar (145 to 8340 psi) |
A 45° angled threaded fitting changes piping direction more gently, reducing turbulence and pressure loss. A 90° fitting provides a sharp turn for navigating obstacles or fitting specific layouts. |
| Stainless steel swivel joint fittings | Allow rotational movement to prevent stress on pipe connections. | 1 to 400 bar (14.5 to 5800 psi) | Different constructions including straight, tee, and elbow fittings. |
| Stainless steel DIN 11851 dairy fittings | Hygienic fittings used in dairy and food processing applications. | - | Different connection types including threaded, reducer, welded, and hose pillar. |
Selection criteria
- Thread size: Thread size refers to the thread's nominal outer diameter.
- Thread size (smaller): Some threaded fittings (e.g., reducers) have different thread sizes on each threaded connection point.
- Connection type: Most threaded fittings have NPT, UNF, BSP, or metric threads. Some have connections for welding or compression ring connections.
- Seal material: If a threaded fitting has a seal (e.g., FKM), ensure the seal's material is suitable for the application's media. Read our chemical resistance of materials guide to learn more.
- Max pressure at 20 °C/68 °F: Stainless steel threaded fittings pressure ratings can range from less than 10 bar (145 psi) to over 500 bar (7250 psi).
FAQs
What are the pressure ratings for stainless steel threaded fittings?
They can range from less than 10 bar (145 psi) to higher than 500 (7250 psi) bar depending on the fitting.
What thread type is standard in the U.S. for stainless steel fittings?
The National Pipe Thread (NPT) is the standard due to its tapered design for better sealing.
Why choose stainless steel over other materials for threaded fittings?
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, strength, and reliability in harsh environments.











