Recommendations For Using Steam Hoses
Figure 1: Steam hose
Steam hoses play a vital role in industries to transmit steam or hot water from one point to another. These hoses carry pressurized hot water in cleaning applications, thawing, blow-out service, and fire prevention. Steam is highly dangerous and costly to work with; hence it is essential to properly handle the installation,maintenance, and daily use of hoses. This article covers the basic construction of a steam hose, maintenance tips, and the various precautions to be taken while handling a steam hose.
Table of contents
View our online selection of Hoses!
Hose construction
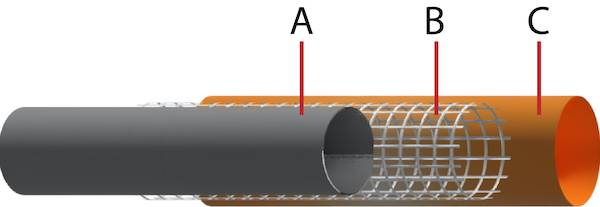
Figure 1: Steam hose parts: Tube (A), reinforcement layer (B), and cover (C)
The materials used in constructing a steam hose must be able to transfer high-temperature steam efficiently along with providing a safe and reliable environment to work on. A typical steel hose consists of three parts: tube, reinforcement layer, and cover.
Tube
The tube (Figure 2 labeled A) is the innermost layer of the hose, and it is made from high-quality black and smooth synthetic rubber, mainly EPDM. This makes it highly resistant to high temperatures and additives. Hence, the hose can deliver steam from one point to another safely and efficiently. The tube comes in contact with the media passing through the hose; hence the choice of material for the tube is vital to ensure the proper functioning of the hose. However, these tubes are not chemically resistant to many chemicals like petroleum products that weaken the pipes and cause early failure. One of the most important criteria for the hose material is the chemical resistance to the media flowing through it. The tube’s inner diameter determines the flow capacity and speed of the flowing media. Read our hosing and tube material article for more information.
Reinforcement layer
The reinforcement layer (Figure 2 labeled B) is situated around the tube and protects the steam hose externally, resists high internal pressures, and helps to eliminate static charges. This reinforcement layer is comprised of 1-2 layers of highly tensile and strong braided or spiral steel wire. This ensures a solid structure for the hose and ensures it works well in a high-pressure environment.
Cover
The cover (Figure 2 labeled C) is made from high-quality EPDM or chlorobutyl and protects the hose from corrosion, aging, weather changes, chemicals, and high temperatures. The cover protects the hose against mechanical abrasions like bursting, cracking, and accidental flame exposure. The cover can be manufactured as either oil-resistant or non-oil-resistant.
Precautions
Since steam carries a large amount of heat under high pressure, it is important to handle steam hoses with care to prevent severe burns or fatalities to the user. Since high-pressure steam is invisible to the human eye, always perform the following checks to ensure a safe operation with steam hoses:
- Never use a steam hose for temperatures and pressures higher than it is rated to handle. If the rated pressure of the hose is exceeded, the hose may burst or create a blow-off in the fitting.
- Check for mechanical abrasions on the hose, specifically rubber pellets on the hose cover or hose braid. An exposed reinforcement can cause rust and accelerated damage, leading to a hose burst. Read our article on steam hoses to know more about the common damages occurring on these hoses in the long run.
- Always check for steam leakages near hose fittings or other parts of the hose because steam carries a large amount of high pressure, which can pose a danger to the user. A loose clamp connection can cause steam leakage; switching to press sleeves can provide a safer working environment as it closes the area between gripper clamps, which is prone to leak.
- Do not touch hose fittings or hose assembly when under pressure for personal security. Always get the assistance of trained personnel while repairing or reworking the hose assembly.
- Check if the hose assemblies are safely installed and fitted, and look into the hose length between the connection points to ensure proper pressure distribution across the length.
- Examine any flattening of the steam hose to prevent damage in the long run. A decrease in flow may indicate swelling of the internal layer of the hose.
Maintenance of steam hoses
Perform the following checks on steam hoses to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the hose:
- Perform periodic checks on the steam hose for blisters and lumps on the hose cover. Inspect the hose thoroughly during fitting installation to ensure there is no damage.
- Look for kinked areas on the hose that can damage the hose in the long run. Use vertical outlets to reduce the stress on the hose and bring down the chances of kinks. Avoid practices where the hose assembly is pulled or twisted, leading to a hose bursting or fitting blow-off.
- If the hose assembly is stored over one month without use, it is advisable to rust-proof the metal within the hose. The formation of rust within the hose may lead to steam leakage during transmission.
- Clean the hose regularly and thoroughly after each use. Make it a habit to drain the hose after each use to avoid ‘popcorning’ of the tube. Water particles retained by the hose after use may be heated up by the steam when the hose is operated later, heating the water particles causing their expansion, leading to ‘popcorn-like blisters that explode on the hose’s inner surface. Popcorning can be avoided by thorough blow-drying of the steam hose after each use or by using extruded inner walls that prevent the collection of water vapor inside the hose.
- Store the hose in proper shape and never bend it beyond its minimum bend radius (given in the hose specifications). Also, never stack heavy objects over the hose, which can ultimately break or damage the hose.
- If a hose assembly has been in use for two years, it is recommended to replace it with a new one. A hose stored in good shape might deteriorate during storage; hence it is advisable to inspect a hose before using it if the hose has not been in use continuously for months.
FAQs
Why does my steam hose fail suddenly?
If the steam hose fails suddenly without any apparent reason, it is primarily due to the change in steam conditions.
How to choose the sizing of hose material for a particular steam application?
Check for the inner and outer diameter of the hose, assembly length, and end connection sizes while choosing a hose.










